Running an Express GraphQL Server
The simplest way to run a GraphQL API server is to use Express, a popular web application framework for Node.js. You will need to install two additional dependencies:
npm install express express-graphql graphql --save
Let's modify our “hello world” example so that it's an API server rather than a script that runs a single query. We can use the 'express' module to run a webserver, and instead of executing a query directly with the graphql function, we can use the express-graphql library to mount a GraphQL API server on the “/graphql” HTTP endpoint:
var express = require('express');
var { graphqlHTTP } = require('express-graphql');
var { buildSchema } = require('graphql');
// Construct a schema, using GraphQL schema language
var schema = buildSchema(`
type Query {
hello: String
}
`);
// The root provides a resolver function for each API endpoint
var root = {
hello: () => {
return 'Hello world!';
},
};
var app = express();
app.use(
'/graphql',
graphqlHTTP({
schema: schema,
rootValue: root,
graphiql: true,
}),
);
app.listen(4000, () => {
console.log('Running a GraphQL API server at localhost:4000/graphql');
});
You can run this GraphQL server with:
node server.js
Since we configured graphqlHTTP with graphiql: true, you can use the GraphiQL tool to manually issue GraphQL queries. If you navigate in a web browser to http://localhost:4000/graphql, you should see an interface that lets you enter queries. It should look like:
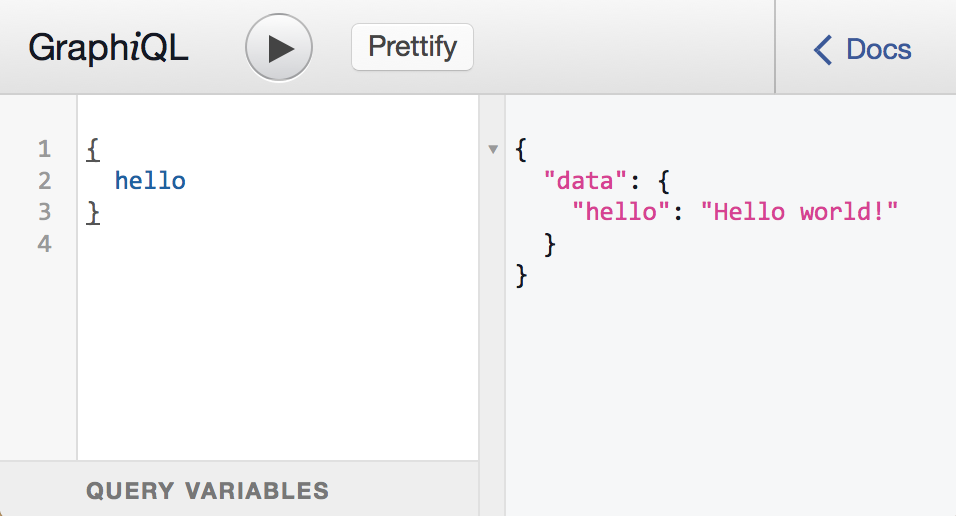
This screen shot shows the GraphQL query { hello } being issued and giving a result of { data: { hello: 'Hello world!' } }. GraphiQL is a great tool for debugging and inspecting a server, so we recommend running it whenever your application is in development mode.
At this point you have learned how to run a GraphQL server and how to use GraphiQL interface to issue queries. The next step is to learn how to issue GraphQL queries from client code.